Overview – Amine gas treating systems
-
Prepare natural gas for commercialization
Custom and standard Amine gas treating systems remove CO2 and H2S, resulting in gas with <2-mol% CO2 and <4-ppm H2S. Efficiently removing CO2, H2S, and mercaptans makes the gas suitable for transportation and use.
The amine plant can be installed as a stand-alone component or as a part of an integrated processing system. We can custom engineer solutions for amine recirculation rates above 700 galUS/min [2.64 m3/min], and we offer five standardized designs for rates below 700 galUS/min. Years of gas sweetening expertise is built into the design and engineering of our standardized gas plants. So you can expect to achieve performance comparable to a custom-designed sweetening plant.
-
Amine treating advantages
- Various heat sources (direct-fired, waste heat, hot oil, and steam systems) can be used for the still reboiler.
- Customized plants can be designed to customer specification while maintaining fast delivery.
- Our amine systems can meet required CO2 and H2S levels operating with multiple solvent types and recirculation rates.
- Standard system designs reduce manufacturing and commissioning times.
- Amine systems are easily combined with other technologies into hybrid systems for many sizes of gas sweetening projects.
Application of Amine gas treating systems
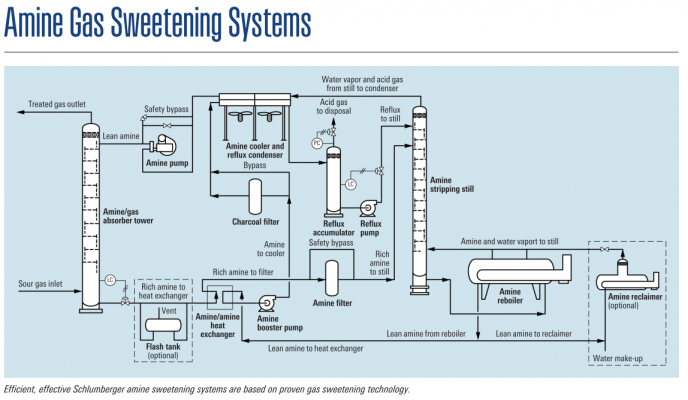
Amine sweetening process as following:
- Sour gas enters the contactor tower and rises through the descending amine solution.
- Purified gas flows from the top of the tower.
- The amine solution, carrying absorbed acid gases, leaves the tower for the heat exchanger or optional flash tank.
- Rich amine is heated by hot regenerated lean amine in the heat exchanger.
- Rich amine is further heated in the regeneration still column, by heat supplied from the reboiler.
- Steam and acid gases separated from the rich amine are condensed and cooled, respectively, in the reflux condenser.
- Condensed steam is separated in the reflux accumulator and returned to the still. Acid gases may be vented, incinerated, or directed to a sulfur recovery system.
- Hot regenerated lean amine is cooled in a solvent aerial cooler and circulated to the contactor tower, completing the cycle.
- A variety of heat sources can be used for the still reboiler—direct fired, waste heat, hot oil, and
steam systems.
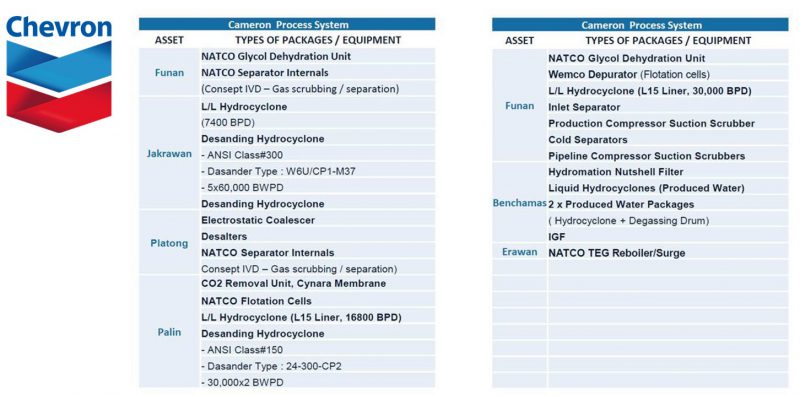
Project Reference

Brochure
Download